[Codility] Stacks and Queues - StoneWall 풀이
예문
https://app.codility.com/programmers/lessons/7-stacks_and_queues/stone_wall/
You are going to build a stone wall. The wall should be straight and N meters long, and its thickness should be constant; however, it should have different heights in different places. The height of the wall is specified by an array H of N positive integers. H[I] is the height of the wall from I to I+1 meters to the right of its left end. In particular, H[0] is the height of the wall’s left end and H[N−1] is the height of the wall’s right end.
The wall should be built of cuboid stone blocks (that is, all sides of such blocks are rectangular). Your task is to compute the minimum number of blocks needed to build the wall.
Write a function:
class Solution { public int solution(int[] H); }
that, given an array H of N positive integers specifying the height of the wall, returns the minimum number of blocks needed to build it.
For example, given array H containing N = 9 integers:
H[0] = 8 H[1] = 8 H[2] = 5
H[3] = 7 H[4] = 9 H[5] = 8
H[6] = 7 H[7] = 4 H[8] = 8
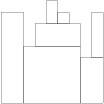
the function should return 7. The figure shows one possible arrangement of seven blocks.
Write an efficient algorithm for the following assumptions:
N is an integer within the range [1..100,000];
each element of array H is an integer within the range [1..1,000,000,000].
해석
- 돌담 : N 미터 길이, 두께는 일정
-
- 다른 곳에 다른 높이를 가져야 함.
- 배열 H : 돌담의 높이가 적힌 양의 정수 N으로 구성 됨
- H[i] : 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 i 에서 i + 1까지의 벽의 높이
- H[0] : 벽의 왼쪽 끝의 높이
- H[N-1] : 벽의 오른쪽 끝의 높이
- 벽은 직육면체로 지어야 한다.
- 각 블록의 모든 면은 직사각형
- 돌벽을 모두 짓는데 필요한 최소 블럭 수를 반환하라.
풀이
- 돌담을 구성하는데 필요한 최소 블럭을 구하기
- 돌담의 이전 높이를 기준으로 현재 높이가 낮으면 현재 높이 기준으로 기준점이 낮춰지고 이전 높았던 높이는 별개의 블럭이 되면서 제거 된다.
- 현재 높이 보다 이전 블럭이 낮아질때까지 계속 제거 해 나감.
- 현재 높이랑 이전 블럭이 같으면 같은 블럭으로 통합 가능 하기 때문에 그냥 유지함.
- 이전 높이 보다 현재 높이가 높으면 카운트 증가, 스택 추가
- 이전 높이 보다 현재 높이가 적으면 높아질 때까지 스택 제거
제약사항
- N의 범위는 정수 [0..100,000]
- 배열 H 의 요소의 범위는 [0..1,000,000,000]
코드
import java.util.Stack;
public int solution(int[] H) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < H.length; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() > H[i]) {
stack.pop();
}
if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek() < H[i]) {
stack.push(H[i]);
count++;
}
}
return count;
}